Did you know that your website’s URL structure can significantly impact your SEO? It’s true! In WordPress, the way your links are structured is managed through a feature called permalinks. When I first started optimizing websites, I underestimated how important these little details were. But trust me, setting up SEO-friendly URLs in WordPress is a game-changer. In this post, I’ll walk you through what permalinks are, why they matter for SEO, and how to configure them to improve your site’s visibility and user experience.
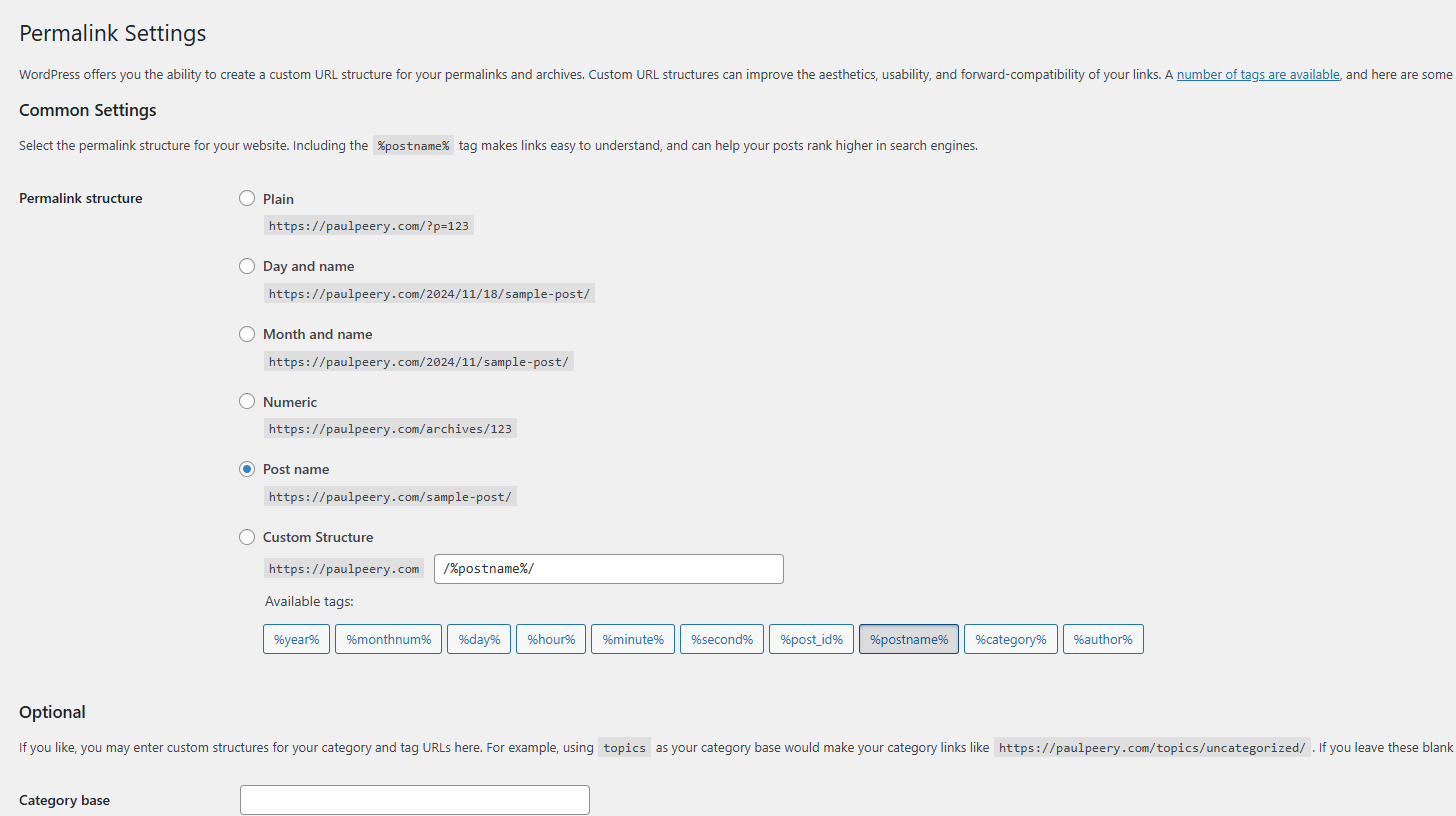
Table of Contents
What Are Permalinks in WordPress?
If you’ve ever clicked on a blog post or navigated to a specific page on a website, you’ve interacted with a permalink—whether you realized it or not. A permalink, short for “permanent link,” is the full URL that takes you to a specific page, post, or resource on your WordPress site. Think of it as the unique address for each piece of content on your website.
When I first started using WordPress, I didn’t give much thought to permalinks. I mean, as long as they worked, why worry, right? Well, it turns out they’re more important than they seem. Permalinks not only tell users where to find your content but also help search engines understand what your page is about.
The Role of Permalinks in Website Functionality
Permalinks serve two main purposes:
- Navigation: They allow users to access your content quickly and directly. Whether someone clicks a link in a Google search result or shares your post on social media, they’re using the permalink to find your content.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): A well-structured permalink can improve your page’s visibility in search engine rankings. It provides search engines with key context about the content of the page.
Examples of Permalink Structures
WordPress offers several default permalink structures, such as:
- Plain: https://example.com/?p=123 (Not ideal for SEO)
- Day and Name: https://example.com/2024/11/18/post-title/
- Month and Name: https://example.com/2024/11/post-title/
- Post Name: https://example.com/post-title/ (Most SEO-friendly)
The first structure, “Plain,” is functional but terrible for SEO because it doesn’t provide any information about the page’s content. On the other hand, the “Post Name” structure is concise, easy to read, and optimized for search engines—a win-win!
Why Permalinks Matter for SEO
Search engines prioritize URLs that are clean, descriptive, and user-friendly. Imagine you’re searching for “WordPress SEO tips,” and you see two URLs:
- https://example.com/?p=456
- https://example.com/wordpress-seo-tips/
Which one would you click on? The second URL clearly tells you what the page is about, making it more likely to attract clicks—and search engines notice this too.
Why SEO-Friendly URLs Matter for Your Website
When I first heard about SEO-friendly URLs, I thought, “Does it really make that much of a difference?” Spoiler alert: It absolutely does. The way your URLs are structured can significantly impact both how search engines rank your content and how users interact with your site.
Let’s break down why this matters and how getting your URL structure right can help your WordPress site thrive.
1. Search Engine Visibility
Search engines like Google analyze your URLs for clues about your content. A well-crafted permalink provides them with the context they need to index your page correctly. For example:
- A URL like https://example.com/best-seo-tools/ instantly communicates that the page is about SEO tools.
- Contrast that with https://example.com/?p=5678/, which offers no useful information to search engines or users.
Using descriptive keywords in your URLs can improve your chances of ranking higher in search results. It’s a small tweak that pays off big time in SEO terms.
2. User Experience
We’ve all clicked on links before and thought, “Wait, where is this taking me?” Clear and concise URLs eliminate that guesswork, making your site more user-friendly. Imagine these two URLs:
- https://example.com/guide-to-wordpress-permalinks/
- https://example.com/?id=8483&cat=12/
The first URL is not only easier to read but also inspires confidence that users are heading to the right content. When users have a smooth experience, they’re more likely to stay on your site longer—and that’s another ranking factor search engines love.
3. Better Click-Through Rates (CTR)
Clean, descriptive URLs are more likely to attract clicks, especially in search results and social media shares. Here’s an example:
- If a user searches for “how to optimize URLs in WordPress,” they’re much more likely to click on https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls-wordpress/ than something like https://example.com/?p=232.
A higher click-through rate signals to Google that your content is relevant, which can boost your rankings over time.
4. Trust and Credibility
Let’s face it: URLs riddled with numbers, symbols, and gibberish just look sketchy. On the other hand, a URL like https://example.com/best-wordpress-tips/ looks professional and trustworthy. Users are more likely to click on links they trust, especially when shopping online or researching topics.
5. Social Media Sharing
When someone shares your content on platforms like Facebook or Twitter, the URL is often visible. An SEO-friendly permalink not only looks clean but also reinforces what the shared content is about, encouraging more clicks.
Quick Pro Tip: Keep Your URLs Short and Sweet
While including keywords in your permalink is crucial, don’t overdo it. Long URLs can look cluttered and off-putting. Aim for a balance between descriptive and concise. For example:
- ✅ https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls-wordpress/
- ❌ https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls-for-wordpress-and-how-to-optimize-them/
By taking the time to optimize your URLs, you’re not just helping search engines understand your content—you’re creating a better experience for your users, which is what truly counts in the long run.

Default Permalink Structures in WordPress Explained
When you install WordPress, it comes with default settings for permalinks. These structures dictate how your URLs are formatted, and while they work out of the box, not all of them are great for SEO or usability. In this section, I’ll break down each of the default permalink structures, their pros and cons, and why you might want to change them.
1. Plain Permalink
Example: https://example.com/?p=123
This is the default permalink structure WordPress assigns to new sites. It uses a query string (like ?p=123) to identify each post or page. While it’s functional, it’s far from user-friendly or SEO-friendly. Neither users nor search engines get any useful information from this format.
- Pros: Simple, guaranteed to work on all servers.
- Cons: Offers no context about the page content, which is bad for both SEO and user experience.
2. Day and Name Permalink
Example: https://example.com/2024/11/18/post-title/
This structure includes the exact date (year, month, and day) followed by the post title. It’s commonly used by news sites or blogs that rely heavily on daily updates.
- Pros: Great for time-sensitive content like news or announcements.
- Cons: Can make your content feel outdated quickly. Imagine seeing a 2018 date on a blog post—it might discourage users from clicking, even if the content is still relevant.
3. Month and Name Permalink
Example: https://example.com/2024/11/post-title/
Similar to the “Day and Name” structure but without the specific day, this format organizes posts by month and title. It’s slightly cleaner but still ties your content to a time frame.
- Pros: Useful for blogs with frequent updates, provides some chronological context.
- Cons: Still not ideal for evergreen content, as the date may deter users looking for up-to-date information.
4. Numeric Permalink
Example: https://example.com/archives/123/
This structure uses numbers to identify content. It’s similar to the “Plain” format but adds the term archives to the URL.
- Pros: Simple and technical.
- Cons: Just like the “Plain” structure, it offers no SEO value or user-friendly context.
5. Post Name Permalink
Example: https://example.com/post-title/
This is the most commonly recommended structure for blogs, portfolios, and businesses looking to improve their SEO. It focuses on the title of the post, making URLs clean, descriptive, and keyword-rich.
- Pros: Best for SEO and user experience. It’s concise and tells users exactly what to expect.
- Cons: Requires you to carefully choose post titles to avoid duplicate or overly long URLs.
6. Custom Structure
Example: https://example.com/category/post-title/ or https://example.com/topic/post-name/
WordPress also allows you to create a custom URL structure using tags like %category%, %postname%, %year%, etc. This is ideal for sites with unique organizational needs, such as e-commerce stores or large content hubs.
- Pros: Flexible and can be tailored to your specific needs.
- Cons: Requires some technical knowledge and a clear plan for structuring your site.
Which Permalink Structure Should You Choose?
For most websites, the Post Name structure (/post-title/) is the best choice. It’s clean, simple, and SEO-friendly. However, if you run a news site or need a chronological archive, a date-based structure might make more sense.
How to Check Your Current Permalink Structure
If you’re not sure which structure your site is using:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings > Permalinks.
- You’ll see the current setting highlighted, along with options to change it.
Understanding these default structures is the first step in optimizing your URLs.
Choosing the Best Permalink Structure for SEO
Selecting the right permalink structure for your WordPress site is a foundational step in optimizing your website for both search engines and users. With so many options available, you might wonder, “Which one should I choose?” Don’t worry—I’ve been there too, experimenting with different setups to find what works best. Let’s walk through how to choose the best permalink structure to supercharge your SEO.
1. Why “Post Name” is a Popular Choice
The “Post Name” structure (https://example.com/post-title/) is the most commonly recommended option for good reason:
- SEO-Friendly: It allows you to include your target keywords directly in the URL.
- User-Friendly: Short, descriptive URLs are easier to remember and share.
- Clean and Professional: This format gives your site a polished, organized appearance.
For example, if your blog post is about “SEO-friendly URLs,” a permalink like https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls/ tells users and search engines exactly what to expect.
2. When to Use Custom Structures
While “Post Name” is a safe bet for most sites, some situations call for a custom structure. Here are a few examples:
- Category-Based Blogs: If your site covers multiple topics, including the category in your URL can help with organization. Example: https://example.com/category/post-title/
- Date-Based Archives: For news or event-based sites, adding the date provides helpful chronological context. Example: https://example.com/2024/11/18/post-title/
- E-commerce Stores: Product URLs might benefit from including categories for better organization. Example: https://example.com/shop/category/product-name/
When creating a custom structure, make sure it stays concise and avoids unnecessary elements.
3. Avoid These Common URL Pitfalls
Choosing a permalink structure isn’t just about what to include—it’s also about what to avoid. Here are a few common mistakes to steer clear of:
- Using “Plain” or Numeric Structures: These formats (https://example.com/?p=123) offer no SEO value and look unprofessional.
- Overloading with Keywords: While keywords are important, stuffing them into your URL can look spammy. Example: https://example.com/seo-tips-seo-friendly-seo-guide/
- Including Dates for Evergreen Content: If your content is meant to stay relevant over time, avoid date-based URLs that can make it look outdated.
4. Tips for Crafting SEO-Friendly Permalinks
Here’s a checklist to ensure your permalinks are optimized:
- Include Keywords Naturally: Use 1-2 primary keywords that describe the content of your page.
- Keep It Short: Avoid long, unwieldy URLs. Aiming for 50-60 characters is a good rule of thumb.
- Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Avoid underscores, as search engines treat them differently.
- Avoid Stop Words: Words like “the,” “and,” or “of” aren’t necessary in most URLs. For example:
- ✅ https://example.com/seo-tips/
- ❌ https://example.com/the-best-seo-tips-you-can-use/
5. How to Update Your Permalink Structure
If your current permalink setup isn’t ideal, you can easily change it in WordPress:
- Go to your WordPress Dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings > Permalinks.
- Select your preferred structure, such as “Post Name” or a custom format.
- Click Save Changes.
Important: If your site is already live, changing the permalink structure can break existing links. To avoid this:
- Use a redirect plugin like Redirection to map old URLs to new ones.
- Update your sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console.
6. When in Doubt, Test Your Changes
After updating your permalinks, take a moment to test your URLs:
- Internal Links: Click through your site to ensure all links are working correctly.
- External Links: Use tools like Ahrefs or Google Analytics to track broken links and update them.
Pro Tip: Keep User Intent in Mind
Ultimately, your goal is to make your URLs clear and helpful for users. Think about what they would type into Google to find your content, and let that guide your permalink decisions.
How to Change Permalink Settings in WordPress
Switching to a more SEO-friendly permalink structure is one of the easiest ways to optimize your WordPress site. If you’re new to WordPress, this process might seem a bit daunting, but trust me, it’s straightforward. I’ll guide you step-by-step so you can confidently update your settings without breaking anything.
1. Understanding the Permalink Settings Page
Before diving into the how-to, let’s take a quick look at the permalink settings page. This is where WordPress allows you to customize your URL structure.
To find it:
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings > Permalinks from the sidebar.
You’ll see several options for permalink structures, ranging from the default “Plain” format to custom setups. This is your control center for all things URL-related.
2. How to Change Your Permalink Structure
Here’s a step-by-step guide to updating your permalink structure:
- Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard Access your WordPress site’s admin panel by adding /wp-admin to your URL (e.g., https://example.com/wp-admin).
- Go to the Permalink Settings In the dashboard sidebar, go to Settings > Permalinks.
- Select a New Structure You’ll see several options:
- Plain: https://example.com/?p=123 (Not recommended)
- Day and Name: https://example.com/2024/11/18/post-title/
- Month and Name: https://example.com/2024/11/post-title/
- Numeric: https://example.com/archives/123/
- Post Name: https://example.com/post-title/ (Best for SEO)
- Custom Structure: Create your own format using tags like %postname% or %category%.
- For most sites, I recommend selecting Post Name.
- Save Your Changes After selecting your preferred structure, click Save Changes at the bottom of the page. WordPress will automatically update your URLs.
3. Setting Up a Custom Permalink Structure
If you need a custom structure, you can build one using WordPress tags. Here are some popular tags you can use:
- %postname% – The name of your post or page (e.g., /seo-tips/).
- %category% – The category assigned to the post (e.g., /seo/seo-tips/).
- %author% – The author’s username.
- %year%, %monthnum%, %day% – The publication date.
For example:
- Blog with Categories: /category/post-title/
- E-commerce Store: /shop/product-name/
Just enter the desired structure into the Custom Structure field and save your changes.
4. Redirecting Old URLs
If you’re changing the permalink structure on an existing site, you’ll need to set up redirects to avoid broken links. A broken link can frustrate users and hurt your SEO.
Here’s how to do it:
- Install a plugin like Redirection or Yoast SEO Premium.
- Use the plugin to map your old URLs to the new ones.
- Test the redirects by visiting old URLs and ensuring they lead to the correct new pages.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
After updating your permalink settings, you might encounter some issues. Here’s how to handle them:
- 404 Errors: If your pages return a 404 error, go to Settings > Permalinks and click Save Changes again. This often flushes the permalink cache and resolves the issue.
- Broken Links: Use a broken link checker tool (like Broken Link Checker or Screaming Frog) to identify and fix any issues.
- Slow Performance: If your custom structure is complex, it can slow down your site. Stick to simpler structures for optimal performance.
6. Best Practices for Changing Permalinks
To avoid problems during or after the transition:
- Update Your Sitemap: Use an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO to regenerate your sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console.
- Inform Your Team: If others manage your content, let them know about the changes to avoid confusion when linking to new URLs.
- Monitor Your Analytics: Keep an eye on Google Analytics and Search Console for any dips in traffic or crawl errors.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to update your permalink settings without a hitch.
Customizing URLs for Pages and Posts
While setting a global permalink structure is essential, fine-tuning individual URLs for specific pages and posts can give your site an additional SEO boost. Customizing URLs ensures that each page has a clean, keyword-rich, and user-friendly URL tailored to its content. Let me show you how to do it step by step.
1. Why Customize URLs?
Not every post or page automatically fits perfectly into the global permalink structure. For example:
- Blog posts might need shorter, more focused URLs.
- E-commerce product pages may benefit from including categories or product-specific keywords.
- Pages like “About Us” or “Contact” can often be simplified to https://example.com/about/ or https://example.com/contact/.
Customizing URLs helps:
- Improve click-through rates by making URLs more descriptive.
- Ensure URLs remain concise and keyword-optimized.
- Avoid unnecessary clutter or irrelevant information.
2. How to Edit URLs for Individual Posts and Pages
Customizing a URL in WordPress is straightforward. Here’s how you can do it:
- Create or Edit a Post/Page Open the post or page you want to customize by clicking on Edit in your WordPress dashboard.
- Locate the Permalink Editor Under the post title field, you’ll see the “Permalink” or “URL” section. By default, WordPress generates the URL based on the title of your post.
- Edit the Slug
- The “slug” is the part of the URL that follows your domain. For example, in https://example.com/seo-tips/, seo-tips is the slug.
- Click the Edit button next to the permalink and type in your desired slug. Use keywords relevant to the post or page, keeping it short and descriptive.
- Save Your Changes Once you’ve updated the slug, click OK, then publish or update your post/page to save the changes.
3. Tips for Crafting Custom Slugs
Here are some best practices to follow when creating custom slugs:
- Use Keywords: Include the primary keyword for the post or page. For example, a blog post titled “10 Tips for SEO” could have a slug like seo-tips.
- Keep It Short: Avoid overly long slugs. A clean and concise URL like https://example.com/seo-basics/ is better than https://example.com/all-you-need-to-know-about-seo-basics/.
- Avoid Stop Words: Words like “and,” “of,” or “the” can clutter your URL. For example:
- ✅ https://example.com/content-strategy/
- ❌ https://example.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-content-strategy/
- Use Hyphens, Not Underscores: Search engines prefer hyphens for separating words in URLs. For instance:
- ✅ https://example.com/seo-tips/
- ❌ https://example.com/seo_tips/
4. Customizing URLs for Categories and Tags
If you manage a blog with categories or tags, customizing these URLs can further enhance your site’s organization and SEO.
To Customize Category URLs:
- Navigate to Posts > Categories in your WordPress dashboard.
- Click Edit under the category you want to update.
- Update the slug in the “Slug” field. For example:
- Original: https://example.com/category/uncategorized/
- Updated: https://example.com/category/seo-tips/
- Save your changes.
To Customize Tag URLs:
- Go to Posts > Tags in your dashboard.
- Edit the tag slug just like you would for a category.
5. Redirecting Old URLs After Customization
When you change an individual post or page’s URL, WordPress does not automatically set up a redirect for the old URL. If your site is live, this can lead to broken links and lost traffic. Here’s how to fix it:
- Install a plugin like Redirection or use an SEO plugin such as Yoast SEO Premium to create a 301 redirect.
- Map the old URL to the new one to ensure users and search engines are directed to the correct page.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Here are a few problems you might encounter and how to solve them:
- 404 Errors: Double-check that your new slug is saved correctly and that your permalink settings are updated.
- Duplicate Content: Avoid creating URLs that are too similar, as this can confuse search engines. For example, https://example.com/seo-tips/ and https://example.com/seo-tips-guide/ may compete for rankings.
7. Real-Life Example
Let’s say you write a blog post titled “How to Set Up SEO-Friendly URLs in WordPress.” The default slug might be:
- https://example.com/how-to-set-up-seo-friendly-urls-in-wordpress/
You can simplify it to:
- https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls/
This version is concise, includes the main keyword, and is easier for users to read and remember.
Customizing your URLs for individual posts and pages is a quick way to boost your site’s SEO and user experience.
Avoiding Common URL Mistakes in WordPress
While customizing URLs can improve your site’s SEO and usability, it’s also easy to make mistakes that hurt your rankings or confuse visitors. I’ve learned the hard way that even minor missteps can have significant consequences. Let’s go over some common URL mistakes and how to avoid them.
1. Using Default or “Plain” Permalink Structures
One of the biggest mistakes new WordPress users make is sticking with the default “Plain” permalink structure (https://example.com/?p=123). This format doesn’t convey any information about your content to search engines or users.
- Why It’s a Problem: Lacks keywords, is unprofessional, and isn’t user-friendly.
- Solution: Switch to an SEO-friendly structure like Post Name (https://example.com/post-title/) by going to Settings > Permalinks.
2. Overloading URLs with Keywords
Keyword stuffing in URLs might seem like a good idea for SEO, but it actually does more harm than good. For example:
- Bad URL: https://example.com/seo-tips-seo-tools-seo-strategies/
- Good URL: https://example.com/seo-tips/
- Why It’s a Problem: Search engines see it as spammy, and it creates a poor user experience.
- Solution: Use 1-2 relevant keywords in your URLs and keep them natural.
3. Including Dates in Evergreen Content
While dates can be useful for time-sensitive content like news articles, they aren’t ideal for evergreen content. For example:
- With Date: https://example.com/2022/07/seo-tips/
- Without Date: https://example.com/seo-tips/
- Why It’s a Problem: Dates can make your content look outdated, even if it’s still relevant.
- Solution: Use a structure like Post Name or a custom format that omits dates.
4. Ignoring URL Length
Long, overly complex URLs can confuse users and hurt click-through rates. For example:
- Bad URL: https://example.com/the-complete-guide-to-understanding-and-optimizing-seo-friendly-urls-in-wordpress/
- Good URL: https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls/
- Why It’s a Problem: Long URLs look cluttered in search results and social media shares.
- Solution: Aim for URLs under 60 characters, focusing on clarity and simplicity.
5. Creating Duplicate URLs
Duplicate URLs occur when different links lead to the same content. For example:
- https://example.com/seo-tips/
- https://example.com/category/seo/seo-tips/
- Why It’s a Problem: Confuses search engines, dilutes ranking signals, and creates a poor user experience.
- Solution: Use canonical tags to specify the preferred URL or consolidate duplicate pages.
6. Changing URLs Without Redirects
If you update a URL on a live site, failing to set up redirects can result in broken links and lost traffic.
- Why It’s a Problem: Users and search engines will encounter 404 errors, damaging your SEO.
- Solution: Use a plugin like Redirection to set up 301 redirects from old URLs to new ones.
7. Using Underscores Instead of Hyphens
Underscores (_) are not recognized as word separators by search engines, whereas hyphens (-) are.
- Why It’s a Problem: Search engines may interpret seo_tips as a single word, reducing clarity.
- Solution: Always use hyphens to separate words in your slugs (e.g., seo-tips).
8. Forgetting to Optimize Category and Tag URLs
Leaving default or messy category/tag slugs untouched can lead to confusing URLs, such as:
- https://example.com/category/uncategorized/
- Why It’s a Problem: It looks unprofessional and provides no context to users.
- Solution: Rename your category slugs to something meaningful, like https://example.com/category/seo-tips/.
9. Mixing Uppercase and Lowercase Letters
URLs are case-sensitive, meaning https://example.com/Seo-Tips/ and https://example.com/seo-tips/ could be treated as separate pages.
- Why It’s a Problem: Creates inconsistency and potential duplication issues.
- Solution: Use lowercase letters consistently for all URLs.
10. Not Monitoring and Updating URLs Over Time
Even well-crafted URLs may need occasional updates, especially if your content evolves or you rebrand.
- Why It’s a Problem: Outdated URLs can mislead users or reduce relevance.
- Solution: Regularly audit your URLs to ensure they’re still optimized and relevant. Update old URLs with redirects if necessary.
Pro Tip: Test Your URLs
Before finalizing any URL changes, test them for:
- Readability: Does the URL make sense at a glance?
- Functionality: Do all links work correctly?
- SEO Value: Are the primary keywords included naturally?
Avoiding these common mistakes will set your site up for long-term success.
How Permalinks Impact User Experience and Navigation
When we think about improving our website, we often focus on design, content, or load speed. But did you know that permalinks—the URLs we use for our pages and posts—play a crucial role in shaping user experience (UX) and navigation? A well-structured permalink isn’t just about SEO; it’s about making your site intuitive, trustworthy, and easy to explore.
Here’s how permalinks influence the experience of your visitors and how you can optimize them for seamless navigation.
1. Clear Permalinks Build Trust
When a user clicks on a link, the first thing they see in their browser’s address bar is the URL. A clean and descriptive URL signals that your site is professional and trustworthy. Compare these two examples:
- Confusing URL: https://example.com/?p=5432
- Clear URL: https://example.com/seo-tips/
Which one would you feel more confident clicking on? The second URL not only tells users what to expect but also feels less suspicious, encouraging them to stay on your site.
2. Easy Navigation Encourages Exploration
Permalinks that follow a logical structure help users navigate your site effortlessly. Imagine visiting a recipe website with URLs like this:
- https://example.com/recipes/desserts/chocolate-cake/
With this URL, you can easily infer the structure of the site and explore related categories, like:
- https://example.com/recipes/desserts/
- https://example.com/recipes/
A well-thought-out permalink structure acts like a breadcrumb trail, guiding users to find more of what they’re looking for without getting lost.
3. Shorter URLs Are More User-Friendly
Long and overly complicated URLs can overwhelm users and reduce click-through rates. A concise URL like https://example.com/seo-tips/ is easier to read, remember, and share compared to something like:
- https://example.com/all-you-need-to-know-about-seo-and-how-it-helps-your-website-rank/
Keep your URLs brief, focusing on clarity and simplicity. This small tweak can significantly enhance user experience.
4. Permalinks and Mobile Browsing
With more than half of all internet traffic coming from mobile devices, your URLs need to cater to mobile users. Mobile browsers often truncate long URLs, leaving users with incomplete or confusing information. For example:
- Truncated URL: https://example.com/this-is-a-really-long-url-that-…
By creating short, descriptive permalinks, you ensure that your URLs display clearly, even on smaller screens.
5. Social Media Sharing Made Simple
Have you ever shared a link on social media and thought, “Wow, this URL looks messy”? Users are less likely to share cluttered or confusing links. A clean permalink makes your content look more appealing and shareable on platforms like Twitter or Facebook. For instance:
- Shareable: https://example.com/seo-tips/
- Unappealing: https://example.com/index.php?id=6789&topic=seo%20tips
When users are confident in the URL, they’re more likely to share your content, boosting traffic and engagement.
6. Reducing Frustration with Predictable URLs
A predictable permalink structure saves users from frustration. If a visitor wants to find related posts or higher-level categories, they can manipulate the URL manually. For example:
- URL: https://example.com/recipes/desserts/chocolate-cake/
- To see all desserts, they might try https://example.com/recipes/desserts/.
- To browse all recipes, they could visit https://example.com/recipes/.
If your permalink structure is inconsistent, users who attempt this navigation might encounter errors, leading to a poor experience.
7. Error-Free Links Enhance Credibility
Nothing frustrates a user more than clicking on a link that leads to a 404 error. Proper permalink management ensures that your URLs remain intact, even when you update or migrate your content. Using 301 redirects for any changes helps maintain a seamless experience for visitors.
8. Practical Tips for User-Friendly Permalinks
Here’s how you can optimize permalinks for better UX and navigation:
- Keep Them Simple: Avoid adding unnecessary words, dates, or categories unless they add clarity.
- Make Them Predictable: Stick to a consistent format across your site.
- Use Keywords: Include keywords that help users and search engines understand the content of the page.
- Test Your URLs: Regularly audit your links to ensure there are no broken or outdated URLs.
Real-Life Example: Why This Matters
Imagine you’re searching for tips on how to bake a cake. You find two URLs:
- https://example.com/?p=4895
- https://example.com/recipes/desserts/chocolate-cake/
The second URL immediately tells you it’s a recipe for chocolate cake and that it’s part of a dessert category. It’s easier to understand and encourages exploration of similar content, while the first URL leaves you guessing.
When your permalinks are intuitive and user-friendly, your visitors stay longer, engage more, and are more likely to return.
Advanced Tips: Adding Keywords and Cleaning Up URLs
By now, you’ve got the basics of creating SEO-friendly permalinks down. But if you really want to stand out, it’s time to take things a step further. Fine-tuning your URLs by incorporating strategic keywords and eliminating unnecessary elements can elevate your WordPress site’s SEO and user experience to the next level. Here’s how to do it.
1. The Role of Keywords in URLs
Including relevant keywords in your permalinks gives search engines and users a clear idea of your page’s content. For example:
- Keyword-Rich URL: https://example.com/seo-friendly-urls/
- Generic URL: https://example.com/post123/
The first URL not only looks more professional but also improves your chances of ranking for “SEO-friendly URLs.”
How to Choose the Right Keywords:
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ahrefs to identify keywords relevant to your content.
- Prioritize terms with high search volume and low competition.
- Focus on user intent—what would someone type into Google to find your content?
2. Avoid Keyword Stuffing
While keywords are essential, overloading your URLs with them can harm your SEO. For instance:
- Bad Example: https://example.com/seo-tips-seo-strategies-seo-tools/
- Good Example: https://example.com/seo-tips/
Search engines may view overly keyword-heavy URLs as spammy, so keep it natural and concise.
3. Remove Unnecessary Words
Stop words like “and,” “the,” and “of” often add clutter without contributing value. Compare these URLs:
- With Stop Words: https://example.com/the-best-guide-to-seo/
- Cleaned Up: https://example.com/best-seo-guide/
The second version is shorter, clearer, and still conveys the main idea.
4. Optimize Category and Tag Permalinks
If you use categories and tags, customize their slugs to make them more SEO-friendly. For example:
- Default Category URL: https://example.com/category/uncategorized/
- Optimized URL: https://example.com/category/seo-tips/
Here’s how to do it:
- Go to Posts > Categories or Posts > Tags in your WordPress dashboard.
- Click on Edit for the category or tag you want to update.
- Enter a clean, keyword-rich slug (e.g., seo-tips) and save your changes.
5. Use Redirects When Updating URLs
If you change a URL, always set up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one. This ensures that visitors and search engines are directed to the correct page, preserving your rankings and user experience.
- Plugins to Use: Install Redirection or enable redirects through an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO Premium.
- Test Your Redirects: Visit the old URL to confirm it redirects properly.
6. Keep URLs Consistent Across Your Site
Consistency is key when it comes to creating a professional and easy-to-navigate website. Ensure that all your URLs:
- Follow the same permalink structure.
- Use lowercase letters.
- Separate words with hyphens, not underscores.
For example:
- Consistent: https://example.com/seo-tips/
- Inconsistent: https://example.com/SEOTips/
7. Use Canonical URLs for Duplicate Content
If you have pages with similar or duplicate content, use canonical tags to point search engines to the preferred version. For example:
- If you have URLs like https://example.com/seo-tips/ and https://example.com/blog/seo-tips/, set the canonical tag to indicate which URL should rank.
How to Add Canonical Tags:
- Install an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
- Edit the post or page and specify the canonical URL in the SEO settings.
8. Audit and Clean Up Old URLs
Over time, your site might accumulate outdated or messy URLs. Regular audits help you identify issues and improve your permalink strategy.
Steps to Perform an Audit:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to crawl your site.
- Identify long, cluttered, or irrelevant URLs.
- Update URLs to be more concise and relevant.
- Set up redirects for any changes.
9. Use Descriptive URLs for Media
By default, WordPress generates generic URLs for media files, such as https://example.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/image123.jpg. Instead, rename your files with descriptive keywords before uploading:
- Bad File Name: image123.jpg
- Optimized File Name: seo-tips-infographic.jpg
This improves SEO and makes your media easier to find and share.
10. Test Your URLs Before Publishing
Always double-check your URLs for clarity, accuracy, and SEO value before publishing a post or page. Ask yourself:
- Does the URL clearly reflect the content?
- Is it short and easy to read?
- Does it include the primary keyword naturally?
Real-Life Example: Cleaning Up a URL
Let’s say you have a post titled “The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Mastering SEO in 2024.” The default URL might be:
- https://example.com/the-ultimate-beginners-guide-to-mastering-seo-in-2024/
After cleanup, it could look like:
- https://example.com/seo-beginners-guide/
The updated URL is concise, keyword-rich, and user-friendly.
By applying these advanced tips, you’ll create URLs that are not only optimized for search engines but also designed with your users in mind.
Troubleshooting Permalink Issues in WordPress
Permalink issues can be frustrating and disruptive, especially if they lead to broken links, error pages, or lost traffic. The good news is that most permalink problems in WordPress are relatively easy to fix with the right tools and techniques. In this section, I’ll guide you through common permalink issues and how to resolve them.
1. 404 Errors After Changing Permalink Settings
One of the most common problems occurs when you update your permalink structure, only to find that existing pages return a 404 error. This happens because WordPress hasn’t updated the URL rewrite rules.
How to Fix:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings > Permalinks.
- Click the Save Changes button without making any changes. This action refreshes the rewrite rules.
- Test your URLs to ensure the issue is resolved.
2. Broken Links After Permalink Changes
If you’ve changed your permalink structure on an existing site, old links may no longer work. This can frustrate users and harm your SEO.
How to Fix:
- Set Up 301 Redirects: Use a plugin like Redirection or Yoast SEO Premium to redirect old URLs to the new ones. This ensures users and search engines are directed to the correct pages.
- Update Internal Links: Check your site for internal links pointing to old URLs and update them.
- Check External Links: Use tools like Ahrefs or Google Search Console to identify backlinks pointing to old URLs. Reach out to site owners to request updates where possible.
3. Permalink Changes Not Taking Effect
Sometimes, even after updating your permalink structure, the changes don’t appear on your site.
How to Fix:
- Clear Your Cache: If you’re using a caching plugin like WP Super Cache or W3 Total Cache, clear the cache to ensure the changes are reflected.
- Check Your .htaccess File: Incorrect or missing rewrite rules in the .htaccess file can cause this issue.
- Go to your WordPress installation directory via FTP or your hosting control panel.
Open the .htaccess file and ensure it includes the default WordPress rules: (perl)
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPressSave the file and refresh your site.
4. Mixed or Conflicting URL Formats
If your site uses a mix of URL structures (e.g., some pages use https://example.com/post-name/ while others use https://example.com/?p=123), it can confuse both users and search engines.
How to Fix:
- Standardize Your Structure: Go to Settings > Permalinks and select a single permalink format for your entire site.
- Set Up Redirects: Redirect any non-standard URLs to their updated versions using a 301 redirect.
5. Incorrect Permalink Settings for Custom Post Types
If you’re using custom post types and notice permalink issues (e.g., 404 errors or incorrect URL formats), the problem may be with the custom post type configuration.
How to Fix:
- Check the custom post type code in your theme or plugin.
Ensure the rewrite parameter is properly set. Example: (php)
'rewrite' => array('slug' => 'your-custom-post-type'),- Refresh the permalinks by going to Settings > Permalinks and clicking Save Changes.
6. Duplicate URLs Caused by Categories or Tags
WordPress sometimes generates duplicate URLs for the same content if categories, tags, and posts are not properly configured.
How to Fix:
- Use Canonical Tags: Add canonical tags to your pages to indicate the preferred URL to search engines. Plugins like Yoast SEO handle this automatically.
- Exclude Categories and Tags from Indexing: Prevent categories and tags from being indexed by search engines using a plugin or by updating your robots.txt file.
7. Page Speed Issues Due to Complex Permalinks
Using overly complex custom permalink structures (e.g., including categories, tags, and post IDs) can slow down your site.
How to Fix:
- Simplify your structure to focus on the Post Name format or a clean custom URL.
- Avoid including elements like %category% or %tag% unless absolutely necessary.
8. Server or Hosting Issues
Sometimes, permalink problems stem from your server configuration rather than WordPress itself. For example:
- Apache servers may not have the mod_rewrite module enabled.
- Nginx servers may require additional rules in the configuration file.
How to Fix:
- For Apache Servers: Contact your hosting provider to ensure mod_rewrite is enabled.
For Nginx Servers: Add the following rules to your Nginx configuration file: (bash)
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}9. Testing and Validating Permalink Fixes
Once you’ve resolved your permalink issues, it’s important to test and validate your changes:
- Test Links: Click through your site to ensure all links are working correctly.
- Monitor Google Search Console: Check for crawl errors or issues in the “Coverage” section.
- Run a Crawl Audit: Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to identify any lingering problems.
Pro Tip: Back Up Your Site Before Making Changes
Before updating your permalink settings or modifying files like .htaccess, always back up your site. Use a plugin like UpdraftPlus or rely on your hosting provider’s backup service.
With these troubleshooting steps, you’ll be able to quickly resolve common permalink issues and keep your WordPress site running smoothly.
Best Practices for Long-Term SEO Success
Optimizing your WordPress permalinks is a powerful step, but maintaining that optimization over time is key to sustaining and improving your site’s performance. By following these best practices, you’ll ensure that your URLs remain SEO-friendly, user-focused, and adaptable as your site evolves.
1. Start with the Right Permalink Structure
Choose the most appropriate permalink structure from the outset. For most sites, the Post Name structure (https://example.com/post-title/) is ideal because it’s clean, keyword-rich, and user-friendly.
Pro Tip: Avoid frequent changes to your permalink structure once your site is live, as this can create broken links and confuse search engines.
2. Regularly Audit Your URLs
Over time, your website will grow, and some URLs may become outdated or redundant. Conduct regular audits to identify:
- Long or messy URLs that can be simplified.
- Broken links that need redirects.
- Duplicate URLs caused by categories or tags.
Use tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or Google Search Console to pinpoint problem areas.
3. Monitor Performance with Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how your URLs are performing in search results. Regularly check:
- Crawl Errors: Identify and fix any 404 errors or other issues.
- URL Click Data: See which URLs are driving traffic and which ones need improvement.
- Coverage Report: Ensure all important pages are being indexed correctly.
4. Keep URLs Short and Descriptive
As a rule of thumb, shorter URLs perform better in search results and are easier for users to remember. Aim for 50-60 characters, focusing on:
- Including 1-2 primary keywords.
- Removing unnecessary words (e.g., “and,” “of,” “the”).
5. Use HTTPS for Secure URLs
Search engines like Google prioritize secure websites, and HTTPS is now a ranking factor. If your site isn’t already using HTTPS:
- Purchase an SSL certificate from your hosting provider (or use a free option like Let’s Encrypt).
- Update your site’s settings to reflect the HTTPS protocol.
6. Leverage Canonical Tags
If you have similar or duplicate content, canonical tags tell search engines which version of a URL to prioritize. This helps prevent duplicate content issues and consolidates ranking signals.
How to Implement Canonical Tags:
- Use an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math to automatically add canonical tags to your pages.
7. Optimize New Content for SEO-Friendly URLs
Every time you create a new post or page, pay attention to the URL slug:
- Include Keywords: Use terms that accurately describe the content.
- Simplify: Avoid long or complex slugs.
- Check Consistency: Ensure the URL follows your site’s established structure.
Example:
- Default: https://example.com/2024/11/seo-tips-and-tricks-to-boost-your-traffic/
- Optimized: https://example.com/seo-tips/
8. Use Redirects Wisely
Redirects are essential for managing changes to your URL structure, but they should be used sparingly to avoid slowing down your site.
- 301 Redirects: Use these for permanent changes to a URL.
- 410 Gone: For content you’ve removed and don’t plan to replace, let search engines know it’s gone for good.
Tools like Redirection or built-in SEO plugins make managing redirects simple.
9. Update Your Sitemap
After making changes to your permalinks or adding new content, update your sitemap to ensure search engines can find and index your URLs.
How to Update Your Sitemap:
- Use an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math to automatically generate and update your sitemap.
- Submit the updated sitemap to Google Search Console.
10. Create a Consistent URL Strategy for Teams
If multiple people manage your site, establish guidelines for URL creation. This ensures consistency and prevents issues like duplicate slugs or overly long URLs.
Include Rules For:
- Preferred permalink structure.
- Formatting (e.g., lowercase, hyphens instead of underscores).
- Use of categories or tags.
11. Avoid Over-Optimization
While it’s important to include keywords in your URLs, avoid over-optimizing. Keyword stuffing can make your URLs look spammy and harm your rankings.
Bad Example:
https://example.com/seo-tips-seo-tricks-seo-tools/
Good Example:
https://example.com/seo-tips/
12. Track URL Performance Over Time
Use analytics tools like Google Analytics or Ahrefs to monitor how your URLs are performing. Pay attention to:
- Pages with high bounce rates.
- URLs with low traffic that may need optimization.
- Top-performing pages to replicate success across other content.
13. Avoid Changing URLs Unnecessarily
Once a URL is live and indexed by search engines, avoid changing it unless absolutely necessary. Frequent changes can disrupt your rankings and lead to broken links.
14. Keep Up with SEO Trends
SEO best practices evolve over time, so stay informed about changes to search engine algorithms and URL optimization techniques. Follow industry blogs like:
- Moz
- Search Engine Journal
- Yoast Blog
15. Invest in Speed and Performance
Fast-loading pages improve both user experience and SEO. Ensure your permalink strategy doesn’t slow down your site:
- Avoid overly complex structures.
- Optimize your hosting and caching settings.
By implementing these best practices, you’ll not only keep your WordPress URLs optimized but also build a strong foundation for long-term SEO success.

Helpful Tools and Plugins for SEO-Friendly Permalinks
Optimizing your permalinks for SEO can feel overwhelming, but the right tools and plugins make it easier to create, manage, and refine your URLs. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced WordPress user, these resources will simplify the process and help you maintain an SEO-friendly structure.
1. Rank Math
Best for: Advanced SEO optimization with a user-friendly interface.
Rank Math is a powerful alternative to Yoast SEO, offering similar features with additional customization options. It’s ideal for users looking for more granular control over their URLs.
Key Features:
- Automatically suggests optimized permalink structures.
- Built-in redirect manager for handling URL changes.
- Advanced options for managing custom post type URLs.
How to Use It:
- Install the plugin and follow the setup wizard to configure basic SEO settings.
- Go to Rank Math > General Settings > Links to enable or disable specific permalink options.
2. Yoast SEO
Best for: Comprehensive SEO management, including permalinks.
Yoast SEO is one of the most popular WordPress plugins for optimizing your site’s SEO. It offers a range of tools to ensure your URLs are clean, optimized, and indexed properly.
Key Features:
- Automatically adds canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues.
- Provides suggestions for keyword-rich slugs during content creation.
- Offers settings to strip unnecessary words from permalinks (e.g., “category”).
How to Use It:
- Install and activate the plugin from the WordPress repository.
- Navigate to SEO > Search Appearance > Permalinks to customize settings.
- Use the content editor to refine slugs when creating posts or pages.
3. Redirection
Best for: Managing 301 redirects and fixing broken links.
Redirection is a simple yet effective plugin for handling URL changes without disrupting your site’s SEO. It’s a must-have if you frequently update or restructure your permalinks.
Key Features:
- Create 301, 302, and 410 redirects with ease.
- Automatically detect and fix broken links.
- Log redirect activity to monitor performance.
How to Use It:
- Install and activate the plugin.
- Go to Tools > Redirection to set up new redirects.
- Monitor the log to identify and resolve issues with your URLs.
4. Pretty Links
Best for: URL shortening and tracking.
Pretty Links is designed to create clean, branded links that are easy to share. While it’s often used for affiliate marketing, it’s also great for optimizing permalinks.
Key Features:
- Shorten long URLs into branded, readable links.
- Track clicks to measure performance.
- Organize and categorize links for better management.
How to Use It:
- Install the plugin and access it under Pretty Links in your dashboard.
- Create new links with custom slugs and track their usage over time.
5. All in One SEO (AIOSEO)
Best for: Comprehensive SEO features with easy setup.
AIOSEO is another powerful plugin for managing SEO across your WordPress site. It includes tools for optimizing permalinks, among other features.
Key Features:
- Automatically generates optimized URLs.
- Offers tools for managing breadcrumbs, canonical tags, and sitemaps.
- Customizes permalinks for WooCommerce products.
How to Use It:
- Install the plugin and follow the setup wizard.
- Navigate to Search Appearance > Advanced Settings to refine permalink options.
6. Broken Link Checker
Best for: Identifying and fixing broken links.
Broken Link Checker scans your site for broken URLs, helping you maintain a seamless user experience and avoid SEO penalties.
Key Features:
- Detects broken internal and external links.
- Allows you to edit links directly from the plugin interface.
- Sends notifications for any issues found.
How to Use It:
- Install and activate the plugin.
- Go to Settings > Link Checker to customize scanning preferences.
- Review the results and fix broken links as needed.
7. WP-Optimize
Best for: Performance optimization and database cleanup.
WP-Optimize helps streamline your WordPress database, which can improve permalink performance and overall site speed.
Key Features:
- Removes unnecessary data like post revisions and drafts.
- Optimizes database tables for faster load times.
- Integrates with caching plugins to boost performance.
How to Use It:
- Install the plugin and navigate to WP-Optimize > Database.
- Review optimization options and click Run Optimization.
8. Screaming Frog
Best for: Comprehensive site audits.
Screaming Frog is a desktop tool that crawls your website to identify issues with your URLs, metadata, and other SEO elements.
Key Features:
- Finds broken links and redirect chains.
- Analyzes URL structures for length and keyword usage.
- Generates detailed reports for further optimization.
How to Use It:
- Download the software and input your website URL.
- Use the SEO Spider to crawl your site and identify areas for improvement.
9. Better Search Replace
Best for: Bulk updating URLs after a migration.
If you’ve recently migrated your site or changed your domain, Better Search Replace can help you update old URLs across your site.
Key Features:
- Search and replace URLs in your database.
- Preview changes before applying them.
- Supports serialized data.
How to Use It:
- Install the plugin and navigate to Tools > Better Search Replace.
- Enter the old and new URLs and run the update.
10. SEOPress
Best for: Lightweight SEO management.
SEOPress is a versatile plugin that covers all the essentials for optimizing your WordPress site, including permalinks.
Key Features:
- Automatically generates SEO-friendly slugs.
- Provides tools for managing redirects and canonical URLs.
- Includes support for WooCommerce SEO.
How to Use It:
- Install SEOPress and follow the setup wizard.
- Use the Advanced Settings to fine-tune your permalink structure.
By leveraging these tools and plugins, you’ll be able to optimize and maintain SEO-friendly permalinks with minimal effort.
FAQs
1. What is the best permalink structure for WordPress SEO?
The Post Name structure (https://example.com/post-title/) is widely regarded as the best option for most WordPress sites. It’s concise, user-friendly, and allows you to include relevant keywords in the URL. This structure helps:
- Improve search engine rankings by making URLs keyword-rich.
- Enhance user experience by clearly describing the content of the page.
How to Set It:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Settings > Permalinks.
- Select the Post Name option and save your changes.
2. How do I fix broken permalinks in WordPress?
Broken permalinks usually occur after changing the permalink structure, migrating your site, or deleting content. Here’s how to fix them:
Steps to Resolve:
- Refresh Permalink Settings:
- Go to Settings > Permalinks.
- Click Save Changes without modifying anything.
- Set Up Redirects:
- Use a plugin like Redirection to map old URLs to new ones (301 redirects).
- Check .htaccess File:
- Ensure your .htaccess file contains the correct rewrite rules (WordPress will regenerate these if needed).
- Audit for Broken Links:
- Use tools like Broken Link Checker or Screaming Frog to find and fix broken links.
3. Can I change permalinks without hurting SEO?
Yes, but you need to be careful to avoid losing traffic or damaging your search engine rankings. Follow these best practices:
Steps to Change Permalinks Safely:
- Backup Your Site: Before making any changes, use a plugin like UpdraftPlus to create a full backup.
- Update Your Permalink Settings:
- Go to Settings > Permalinks and choose the new structure.
- Set Up 301 Redirects: Redirect old URLs to their new counterparts to preserve SEO equity.
- Update Your Sitemap: Use an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO to regenerate your sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console.
- Test Links: Ensure all internal and external links are updated and functional.
Conclusion
Optimizing permalinks for your WordPress site is one of the simplest yet most impactful changes you can make for both SEO and user experience. By choosing an SEO-friendly structure, incorporating relevant keywords, and maintaining clean, concise URLs, you can significantly enhance your website’s visibility, trustworthiness, and navigation.
Remember, the goal is not just to create URLs that search engines love, but also to make them intuitive and user-friendly for your audience. Whether you’re starting fresh or refining an existing site, the strategies and tools shared in this guide will set you up for long-term success.
If you have any questions or need further guidance on setting up SEO-friendly permalinks in WordPress, feel free to drop a comment below. And don’t forget to share this guide with anyone who might find it helpful!
External Link: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Starter Guide
